
FiteBac® Antimicrobial
Cavity Cleanser

FiteBac® FT Bond
COMING SOON
Indications for Use: Permanent placement of dental appliances and restorations
Development Status: 510(k) submission Q2/2021
Target Audience: Prescription use for Dental Professionals

FiteBac® CC OrthoSeal
COMING SOON
Indications for Use: Sealant applied to enamel prior to placement of orthodontic bracket adhesive
Development Status: 510(k) submitted Q4/2020
Target Audience: Prescription use for Dental Professionals
How does FiteBac® work?
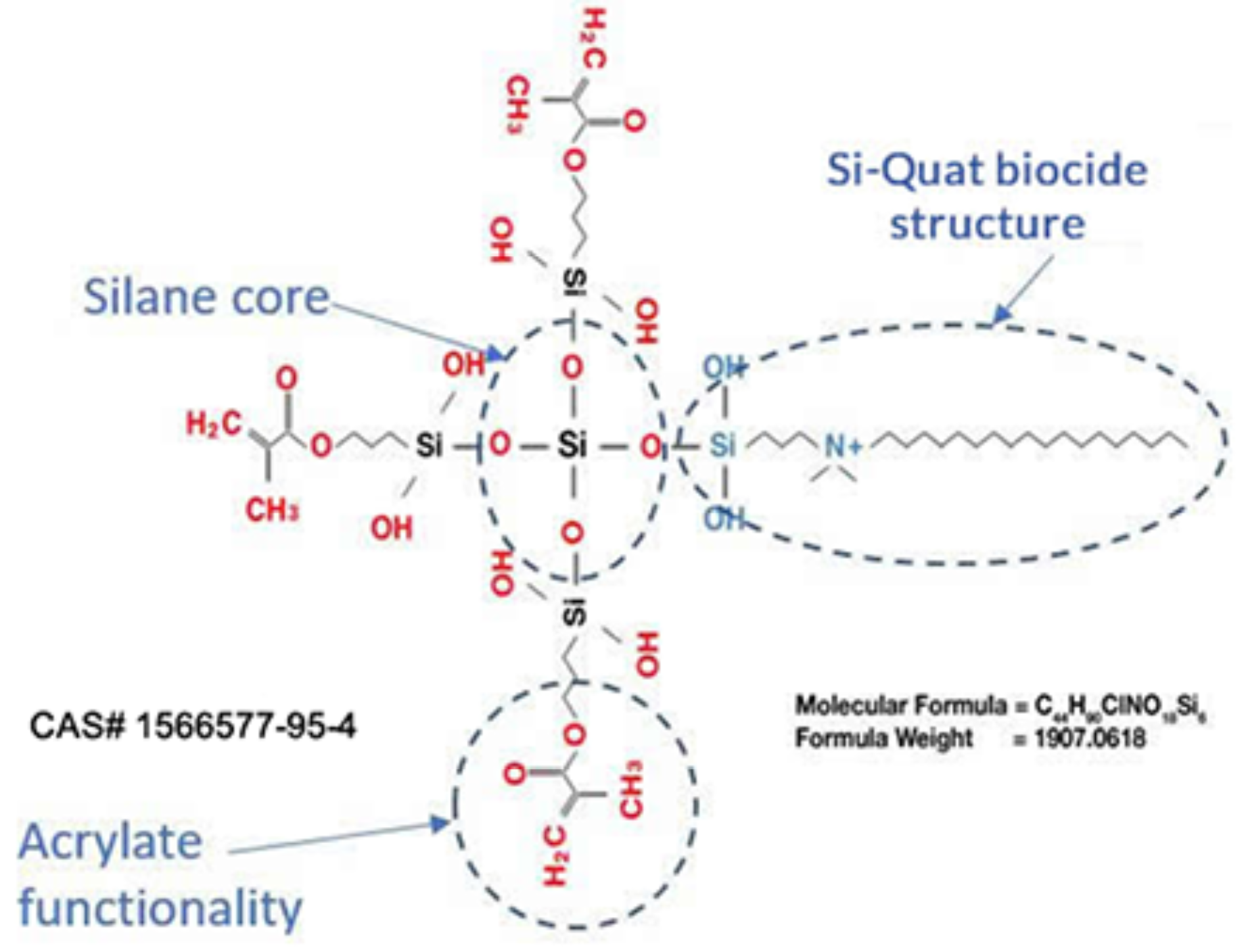
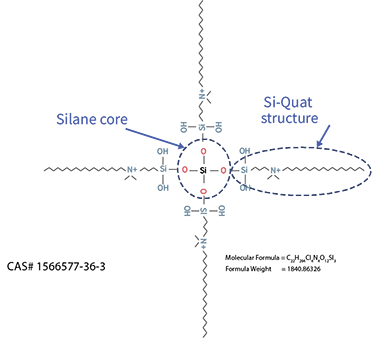
Si-Quat biocide covalently bound to a silane core containing acrylate functionality.
-
Acrylate functionality allows for
co-polymerization within several polymer systems
- Normal wear of a dental device exposes fresh K18 QAMS creating continuous microbiological protection
Patent protection until 2033.
1. Gong SQ, Epasinghe J, Rueggeberg FA, et al. An ORMOSIL-containing orthodontic acrylic resin with concomitant improvements in antimicrobial and fracture toughness properties. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e42355.
- Does not negatively impact adhesive bond strength to dentin2,3
- Excellent antimicrobial activity2,4
- Improves infiltration of adhesive monomers into acid etched dentin2
- Inhibition of MMP-9 and Cathepsin-K2,4
Patent protection until 2033.
2. Gou YP, Li JY, Meghil MM, et al. Quaternary ammonium silane-based antibacterial and anti-proteolytic cavity cleanser. Dent Mater. 2018;34(12):1814-1827.
3. Daood D, Yiu CKY, Burrow MF, Niu LN, Tay FR. Effect of a novel quaternary ammonium silane cavity disinfectant on durability of resin-dentine bond. J Dent. 2017;60:77-86.
4. Umer D, Yiu CK, Burrow MF, Niu LN, Tay FR. Effect of a novel quaternary ammonium silane on dentin protease activities. J Dent. 2017;58:19-27.
Indications for Use: Intended for cleansing and moistening/re-wetting of cavity preparations
Development Status: Cleared for marketing in the United States
Target Audience: Prescription use for Dental Professionals
K-18/Ethanol Pre-Bonding Agent
a.) Enhances bond strength of bonding agents from various companies.
b.) Penetration greater than 100um into etched dentinal tubules helping to occlude tubules
c.) Reduces sensitivity to exposed dentin
d.) Inhibits MMP and Cathepsin activity from etched dentin
e.) Reduces micro-leakage at hybrid layer of restoration produces cell death of bacteria
K18 Additive to Several Bonding Systems
a.) Enhances the bond strength of the systems
b.) Inhibitor of MMP and Cathepsin
c.) Reduces micro-leakage at hybrid layer on dentin Additive to Composite Materials
a.) Significantly reduces acylate shrinkage
b.) Maintains antimicrobial activities throughout composite system
Additive to All Resin and Resin Modified Cement
a.) Enhances durability and toughness
b.) Maintains Antimicrobial
Additive to All Types of Dental Glass Particles by Functionalizing Instead of Silanizing
Additive to all Bis-Acryl, UDMA, PMMA, and Poly R Methacrylates where R represents either Ethyl, Vinyl, Isobutyl
a.) Improved fracture toughness, durability, and flexural strength
Additive to Endodontic Sealers MTA, Epoxy, CaOH, etc.
Dental Varnish After Dental Prophy
K-18 Additive to Glass Ionmer Restoration
a.) Enhances toughness
b.) Antimicrobial throughout materials
